PRP Therapy: A Guide to Breast Tissue Regeneration
Platelet-rich plasma therapy has expanded beyond facial rejuvenation into various aesthetic applications, including breast tissue enhancement. This innovative approach uses concentrated growth factors from your own blood to potentially stimulate collagen production and tissue regeneration. While research continues to evolve, understanding how PRP works, its applications in breast aesthetics, and realistic expectations can help you make informed decisions about this emerging treatment option.
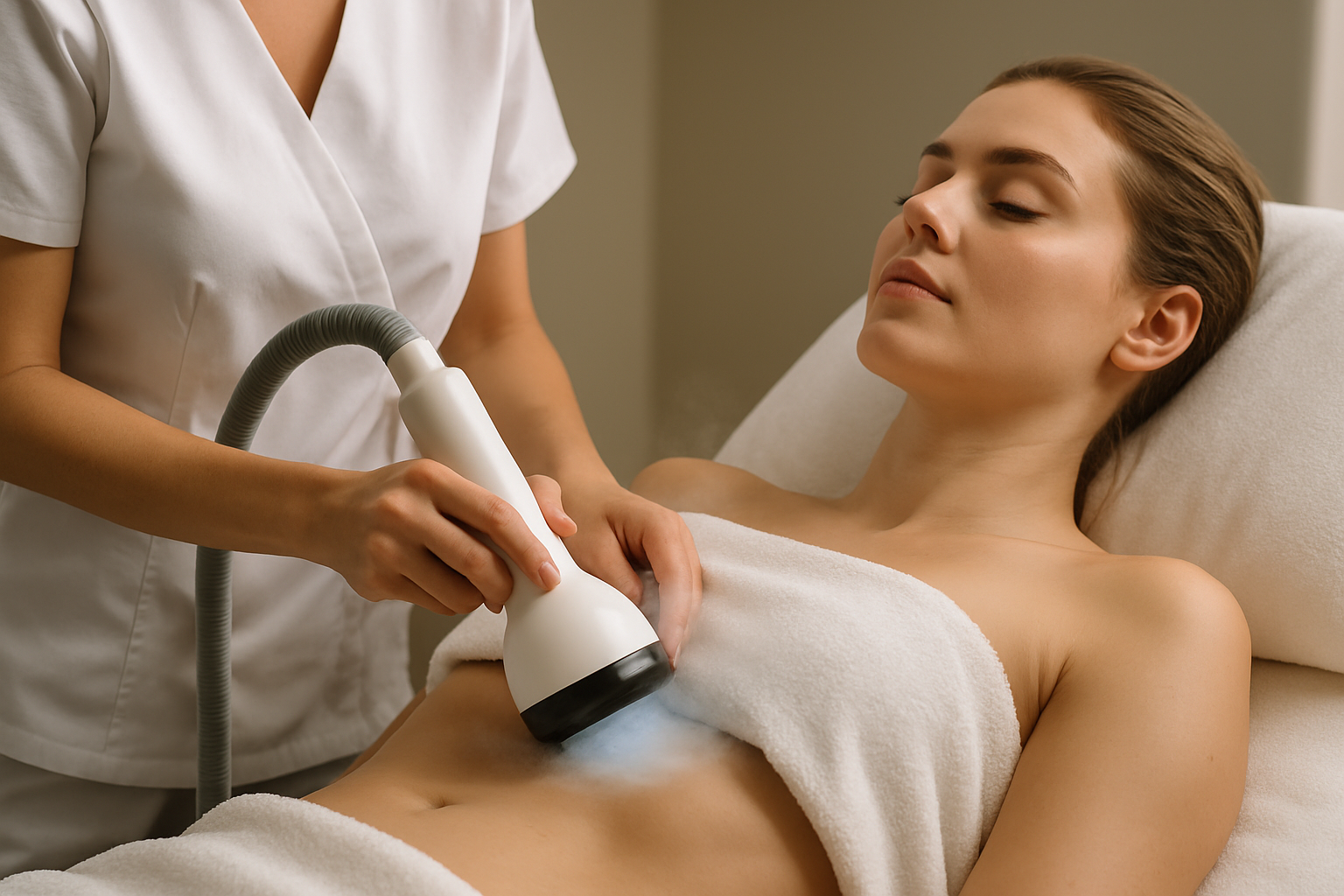

Platelet-rich plasma therapy represents a growing area of interest in aesthetic medicine, particularly for those seeking minimally invasive options for breast enhancement and tissue rejuvenation. This procedure involves extracting a small amount of blood, processing it to concentrate platelets and growth factors, then reinjecting it into targeted areas. The concept builds on the body’s natural healing mechanisms, though scientific evidence regarding its effectiveness for breast enhancement remains limited and requires further investigation.
What Is PRP Breast Enhancement?
PRP breast enhancement involves injecting concentrated platelet-rich plasma into breast tissue with the goal of improving skin quality, texture, and potentially stimulating minor tissue regeneration. The process begins with a blood draw, similar to routine laboratory testing. The blood is then placed in a centrifuge that separates plasma rich in platelets from other blood components. This concentrated plasma contains growth factors that theoretically promote collagen production and cellular renewal. Practitioners inject the PRP into specific areas of the breast, focusing on skin quality improvement rather than significant volume increase. The procedure typically takes 60 to 90 minutes and is performed under local anesthesia. Patients should understand that results vary considerably, and this approach does not provide the dramatic changes associated with surgical interventions. Multiple sessions are usually recommended, though the optimal treatment protocol has not been standardized across the medical community.
Natural Breast Lift Options
For individuals seeking alternatives to surgical breast lifts, several non-invasive or minimally invasive options exist, though each has limitations. Exercise targeting pectoral muscles can improve chest wall support and posture, potentially creating a subtle lifting effect, though it cannot reverse significant tissue sagging. Radiofrequency and ultrasound treatments aim to tighten skin through controlled heating of deeper tissue layers, stimulating collagen remodeling over time. Results are typically modest and require maintenance sessions. Thread lifts involve inserting dissolvable sutures under the skin to provide temporary support, though this technique is more commonly used for facial rejuvenation and has limited application for breast tissue. Topical treatments containing retinoids, peptides, or antioxidants may improve skin quality but cannot address structural sagging. PRP injections fall into this category of non-surgical options, with proponents suggesting it may enhance skin elasticity and firmness. However, patients should maintain realistic expectations, as none of these approaches can replicate the results of surgical mastopexy for moderate to severe ptosis.
Aesthetic Breast Procedures
The landscape of aesthetic breast procedures ranges from minimally invasive treatments to comprehensive surgical interventions. Surgical options include augmentation with implants or fat transfer, mastopexy for lifting sagging tissue, reduction for size decrease, and combination procedures addressing multiple concerns simultaneously. Non-surgical alternatives have expanded in recent years, including laser treatments for skin tightening, injectable fillers for minor volume enhancement, cryolipolysis for fat reduction in surrounding areas, and regenerative approaches like PRP therapy. Each procedure category serves different goals and patient populations. Surgical interventions provide more dramatic and longer-lasting results but involve greater recovery time, potential complications, and higher costs. Minimally invasive treatments offer reduced downtime and lower risk profiles but deliver subtler outcomes that may require repeated sessions. When considering any aesthetic breast procedure, consultation with board-certified plastic surgeons or dermatologists specializing in aesthetic medicine is essential for understanding realistic outcomes, potential risks, and appropriate candidacy.
| Procedure Type | Provider Specialty | Key Features | Cost Estimation |
|---|---|---|---|
| PRP Breast Therapy | Dermatologist, Aesthetic Physician | Minimally invasive, uses own blood, multiple sessions needed | $800 - $2,500 per session |
| Surgical Breast Lift | Board-Certified Plastic Surgeon | Permanent repositioning, significant results, longer recovery | $5,000 - $12,000 |
| Radiofrequency Skin Tightening | Dermatologist, Medical Spa | Non-invasive, gradual results, maintenance required | $1,500 - $4,000 per treatment series |
| Fat Transfer Augmentation | Plastic Surgeon | Natural volume increase, requires liposuction donor site | $4,000 - $10,000 |
| Thread Lift | Aesthetic Physician | Minimally invasive, temporary support, limited breast application | $1,500 - $4,500 |
Prices, rates, or cost estimates mentioned in this article are based on the latest available information but may change over time. Independent research is advised before making financial decisions.
Vampire Facial for Breasts
The term vampire facial gained popularity through celebrity endorsements of PRP facial treatments, and the concept has been adapted for breast applications. Similar to facial PRP procedures, the breast version involves microneedling or injection techniques to deliver platelet-rich plasma into tissue. Microneedling creates controlled micro-injuries in the skin, theoretically enhancing PRP absorption and triggering collagen production as part of the healing response. Proponents claim this combination may improve skin texture, reduce the appearance of stretch marks, and enhance overall breast skin quality. The procedure typically requires numbing cream for comfort, followed by microneedling and PRP application or direct injection. Patients may experience temporary redness, swelling, and bruising lasting several days. While facial PRP has more established research supporting its use for skin rejuvenation, evidence specifically for breast applications remains limited. The treatment does not increase breast size or provide significant lifting of ptotic tissue. Multiple sessions spaced four to six weeks apart are generally recommended, with maintenance treatments suggested annually. As with any aesthetic procedure, selecting qualified practitioners with appropriate training and sterile technique is crucial for safety and optimal outcomes.
Considerations and Realistic Expectations
When evaluating PRP therapy for breast tissue regeneration, several important factors deserve careful consideration. First, scientific evidence supporting its effectiveness for breast enhancement remains preliminary, with most existing research focusing on wound healing and facial applications rather than breast aesthetics specifically. Individual results vary significantly based on age, skin quality, degree of tissue laxity, and overall health status. PRP is not suitable for individuals with significant breast ptosis, those seeking substantial size increase, or patients with certain blood disorders or active infections. The treatment works best for minor skin quality improvements rather than structural changes. Cost considerations are important, as multiple sessions are typically required without guarantee of desired outcomes, and insurance does not cover aesthetic procedures. Potential side effects include bruising, swelling, infection risk, and allergic reactions, though serious complications are rare when performed by qualified practitioners. Alternative treatments may be more appropriate depending on individual goals, and thorough consultation with board-certified specialists helps determine the most suitable approach. Managing expectations realistically prevents disappointment and ensures informed decision-making about aesthetic interventions.
Conclusion
PRP therapy for breast tissue regeneration represents an evolving area within aesthetic medicine, offering a minimally invasive option for those interested in potential skin quality improvements. While the procedure harnesses the body’s natural growth factors and healing mechanisms, scientific evidence specifically supporting its effectiveness for breast enhancement remains limited. Understanding the procedure’s capabilities, limitations, and realistic outcomes helps individuals make informed choices aligned with their aesthetic goals. Consultation with qualified medical professionals, thorough research, and careful consideration of all available options ensure the most appropriate treatment path for individual circumstances and expectations.